Mechanisms and inhibition of Porcupine-mediated Wnt acylation.
Liu, Y., Qi, X., Donnelly, L., Elghobashi-Meinhardt, N., Long, T., Zhou, R.W., Sun, Y., Wang, B., Li, X.(2022) Nature 607: 816-822
- PubMed: 35831507
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-04952-2
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7URA, 7URC, 7URD, 7URE, 7URF - PubMed Abstract:
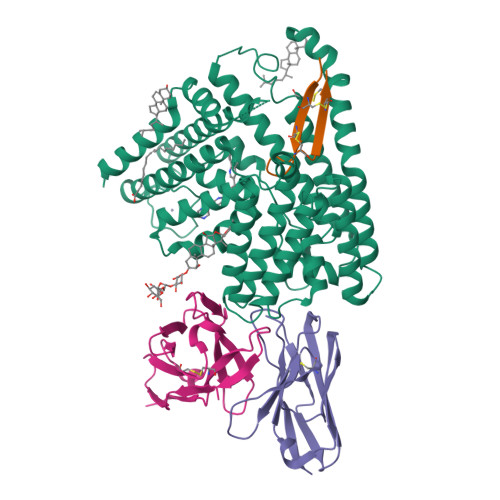
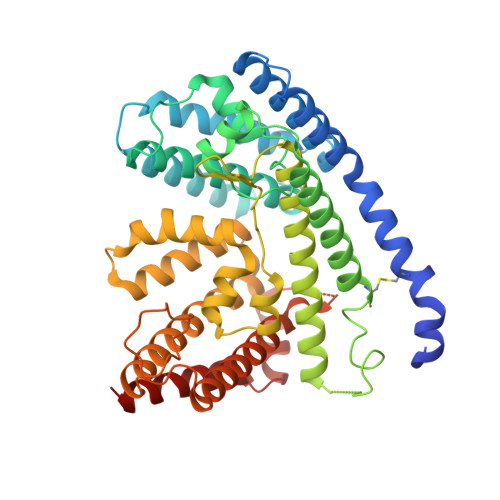
Wnt signalling is essential for regulation of embryonic development and adult tissue homeostasis 1-3 , and aberrant Wnt signalling is frequently associated with cancers 4 . Wnt signalling requires palmitoleoylation on a hairpin 2 motif by the endoplasmic reticulum-resident membrane-bound O-acyltransferase Porcupine 5-7 (PORCN). This modification is indispensable for Wnt binding to its receptor Frizzled, which triggers signalling 8,9 . Here we report four cryo-electron microscopy structures of human PORCN: the complex with the palmitoleoyl-coenzyme A (palmitoleoyl-CoA) substrate; the complex with the PORCN inhibitor LGK974, an anti-cancer drug currently in clinical trials 10 ; the complex with LGK974 and WNT3A hairpin 2 (WNT3Ap); and the complex with a synthetic palmitoleoylated WNT3Ap analogue. The structures reveal that hairpin 2 of WNT3A, which is well conserved in all Wnt ligands, inserts into PORCN from the lumenal side, and the palmitoleoyl-CoA accesses the enzyme from the cytosolic side. The catalytic histidine triggers the transfer of the unsaturated palmitoleoyl group to the target serine on the Wnt hairpin 2, facilitated by the proximity of the two substrates. The inhibitor-bound structure shows that LGK974 occupies the palmitoleoyl-CoA binding site to prevent the reaction. Thus, this work provides a mechanism for Wnt acylation and advances the development of PORCN inhibitors for cancer treatment.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Molecular Genetics, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX, USA.